| Additional remarks phenotype | Mutant/mutation
The mutants (strongly) express GFP in all life cycle stages (under the control of the constitutive and strong hsp70 promoter). The Bergreen mutant does not contain a drug-selectable marker. The gfp-gene has been integrated by double cross-over integration into a silent intergenic region on chromosome 6.
Two plasmids, pBART-SIL6 and pBAT-SIL6, were used to generate the transgenic parasites lines 6GR and 6G.
These plasmids differ in the sequence of a small repeat region that allows removal after negative selection of either the drug-selectable marker alone or both the drug-selectable marker and the gfp gene. In plasmid pBART-SIL6 this is the 5'-UTR of hsp70 (removal of both the drug-selectable marker and gfp). In pBAT-SIL6 this sequence is the 3'UTR of Pbdhfr/ts (removal of the drug-selectable marker.
The plasmids are integrated by double cross-over integration in a locus on P. berghei chromosome 6 between two hypothetical open reading frames (PBANKA_061210 and PBANKA_061220), both displaying only limited gene expression in the stages studied thus far. The integration of pBART-SIL6 and pBAT-SIL6 at this locus was designed to occur 1 kb 3' of PBANKA_061210 and 0.9 kb of PBANKA_260 061220.
After negative selection of 6GR and 6G the following parasite lines were selected: 6rec (no selectable marker, no gfp) and Bergreen (no selectable marker; GFP positive).
Protein (function)
Phenotype
All life cycle stages (strongly) express GFP.
No significant growth defect at any stage of the parasite life cycle, which included asexual and sexual blood stage development, ookinete formation mosquito midgut oocyst formation and growth, salivary gland sporozoite numbers, cultured liver stage development, sporozoite infectivity, and mosquito-to-mouse transition.
The normal phenotypes of all stages indicate that the (high) GFP-expression does not affect the phenotypes and that the integration of gfp into the locus on chromosome 6 is 'phenotypically silent'
Additional information
The plasmids pBART-SIL6 and pBAT-SIL6 are versatile transfection vectors. These targeting vectors, collectively referred to as the Berghei Adaptable Transfection (pBAT) plasmids, contain key elements that permit recycling of the drug-selectable cassette, robust green fluorescent labelling of recombinant parasites, carboxy-terminal tagging of target proteins with a red fluorescent–epitope tag fusion, and expression of heterologous genes. The vectors are optimized for small size, versatile restriction endonuclease recognition sites and potential exchange of individual vector elements. See the figure below for further details.
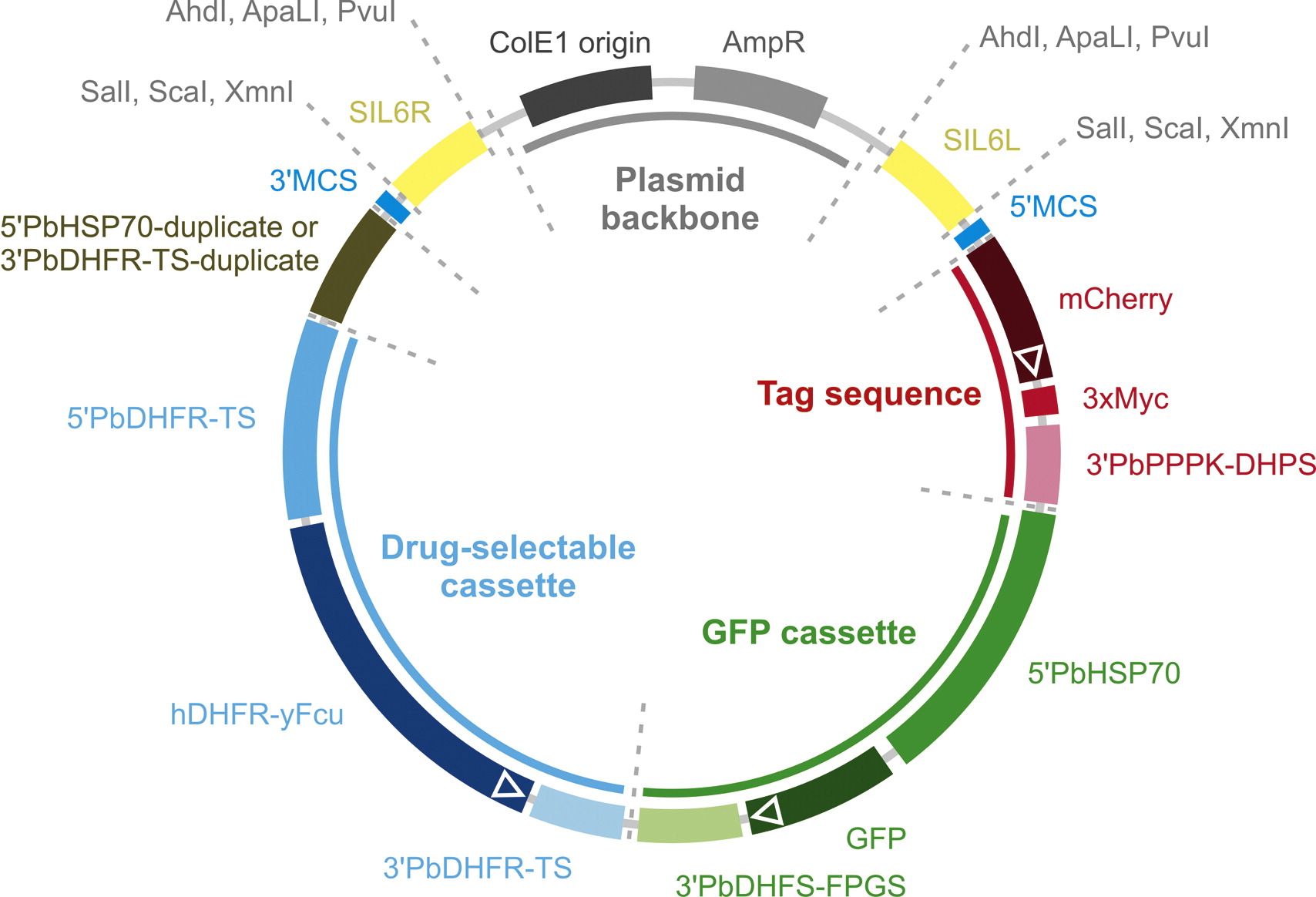
Fig. Schematic representation of the functional DNA elements in pBA(R)T-SIL6. pBA(R)T-SIL6 contains six functional elements that can be used for advanced experimental genetics approaches in P. berghei. All elements are flanked by unique REase recognition sites (Table 1) allowing exchange of the various vector elements. The drug-selectable cassette (blue) Q3 consists of a fusion of human DHFR and yeast Fcu under the control of P. berghei DHFR-TS 5'- and 3'-UTRs. hDHFR confers resistance to pyrimethamine and WR99210 allowing positive selection of successfully transfected parasites. yFcu confers sensitivity to 5-fluorocytosine allowing recycling of the drug-selectable cassette. The high-expressing GFP cassette (green) under the control of P. berghei HSP70 5'-UTR and DHFS-FPGS 3'-UTR allows fluorescence microscopy analysis of life and fixed mutant parasites in all parasite life cycle stages. The cassette can also be used to introduce highly expressed transgenes, with or without a C- or N-terminal GFP tag. The direct repeat sequence (olive) allows recombination after negative selection with 5-fluorocytosine. In pBART-SIL6, a fragment of the PbHSP70 5'-UTR is duplicated, which, following recombination, results in the excision of the drug-selectable and GFP cassettes. In pBAT-SIL6, the PbDHFR-TS 3'-UTR is duplicated, which, following recombination, results in the excision of the drugselectable cassette alone. The tag sequence (red) consists of a gene encoding the red fluorescent protein mCherry and a triple c-Myc epitope tag both preceded by a linker sequence and followed by the P. berghei PPPK-DHPS 3'-UTR. The tag is linked upstream to a large multiple cloning site that enables fusions of genes or promoters of interest to a combined fluorescent protein-epitope tag or to the epitope tag alone. Note that the design allows the combination of a gene knockout strategy with promoter activity testing. Two multiple cloning sites (5'MCS and 3'MCS, blue) with twelve unique REase recognition sites each allow flexible cloning of targeting sequences for ends-out recombination. Two DNA elements (yellow) allow stable integration in a silent intergenic locus on P. berghei chromosome 6 (SIL6). For parasite transfection, vectors can be linearized for integration in SIL6 (AhdI, ApaLI, or PvuI) or via the targeting sequences cloned into the multiple cloning sites (SalI, ScaI, or XmnI) using single REases that also digest the plasmid backbone (grey) thus reducing the risk of episomal transfections.
Four pBAT plasmids are described in this study: pBART-SIL6, pBART, pBAT-SIL6, and pBAT. Elements included in the design of the pBAT plasmid set are: (i) a drug-selectable cassette, (ii) a high expressing GFP cassette, (iii) a C-terminal red fluorescent (mCherry) and triple epitope (3xMyc) tag, (iv) two extensive multiple cloning sites, and, in the case of pBART-SIL6 and pBAT-SIL6, (v) two sequences for stable transgene integration into an silent intergenic locus at a synteny breakpoint on P. berghei chromosome 6 (SIL6). All individual elements, coding sequences, and regulatory regions are flanked by unique REase recognition sites, usually including at least one blunt-cutting REase. This strategy enables straightforward exchange of each of the sequence elements. The sequences of the pBART-SIL6, pBART, pBAT-SIL6, and pBAT vectors have been deposited with GenBank, accession numbers JX099568–JX099571, respectively.
Other mutants
|
 *RMgm-757
*RMgm-757 Transgene: Mutant parasite expressing a transgene
Transgene: Mutant parasite expressing a transgene


